In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are evolving at an unprecedented pace, vulnerability management has emerged as an indispensable component of enterprise security. It’s no longer a luxury but a necessity.
The Imperative for Vulnerability Management
Vulnerabilities, essentially weaknesses in software, systems, or networks, offer attackers entry points. If left unpatched, these can lead to devastating consequences, including data breaches, financial loss, reputational damage, and even operational downtime.
For enterprises, the stakes are particularly high. With vast IT infrastructures, complex systems, and sensitive data, the potential impact of a successful cyberattack can be catastrophic. Vulnerability management, therefore, is not just about protecting systems but safeguarding the entire business.
Core Components of Vulnerability Management
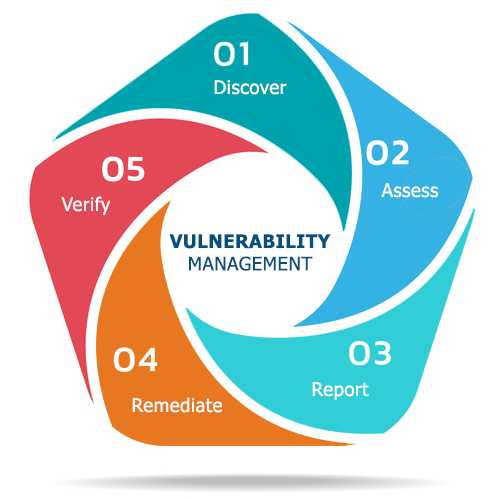
Effective vulnerability management involves several key phases:
- Discovery: Identifying all assets, systems, and applications within the enterprise.
- Assessment: Analyzing systems for vulnerabilities using various tools and techniques.
- Prioritization: Ranking vulnerabilities based on severity, exploitability, and potential impact.
- Remediation: Implementing patches, updates, or configuration changes to address vulnerabilities.
- Verification: Ensuring that remediation efforts have been successful.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly scanning systems for new vulnerabilities and repeating the process.
Best Tools for Vulnerability Management
A robust vulnerability management program relies on a combination of tools and processes. Here are some of the most effective options available:
- Vulnerability Scanners: These tools automatically identify vulnerabilities in systems and applications. Examples include Nessus, OpenVAS, Qualys, and Rapid7.
- Configuration Management Databases (CMDBs): These central repositories of IT assets provide a foundation for vulnerability management by offering a comprehensive view of the environment.
- Patch Management Tools: These tools automate the process of applying software patches and updates.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): While primarily focused on threat detection and prevention, IDPS can also identify vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Assessment and Management (VAM) Platforms: These comprehensive solutions offer a unified approach to vulnerability management, encompassing discovery, assessment, prioritization, remediation, and reporting.
Beyond Tool Selection
While tools are essential, a successful vulnerability management program requires a broader approach. Key considerations include:
- Risk Assessment: Understanding the overall risk landscape and prioritizing vulnerabilities accordingly.
- Staff Training: Ensuring employees are aware of the importance of vulnerability management and know how to report potential issues.
- Incident Response Plan: Having a well-defined plan in place to respond to security incidents.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and refining the vulnerability management process.
In conclusion, vulnerability management is a critical function for enterprises seeking to protect their digital assets. By implementing a robust program, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of cyberattacks and build a stronger security posture.